Video Editor: who they are, what they do and how to become one
Who they are and what they do
The Video Editor is a key professional in the audiovisual production process, responsible for assembling footage into a final product that is coherent and engaging.
Working in close collaboration with the creative team, they help shape the project’s artistic vision, ensuring that each narrative and stylistic choice is enhanced through cinematic editing.
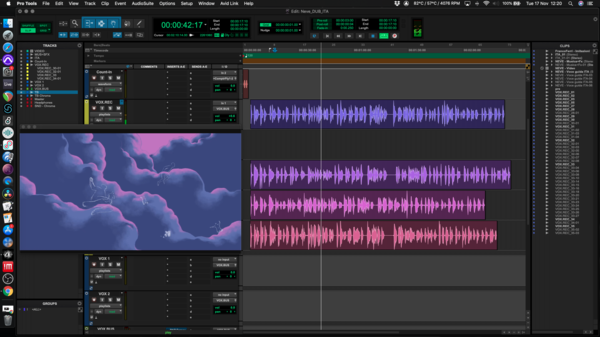
Using professional editing software, the Video Editor selects, cuts, and structures visual sequences, integrating transitions, special effects, graphics, and audio tracks. Their goal is to create an effective and immersive audiovisual experience.
Role and responsability
The Video Editor plays a crucial role in the creation of an audiovisual product. Their work requires technical skills, narrative sensitivity, and the ability to collaborate. Main responsibilities include:
• Footage selection: Reviews available material to identify the most effective shots, discarding those that are technically or narratively weak.
• Narrative editing: Assembles sequences according to a logical temporal and narrative flow, aiming to build a clear, engaging structure that aligns with the Director’s vision.
• Pacing management: Adjusts scene duration to maintain a rhythm appropriate to the story, avoiding unnecessary or repetitive moments.
• Technical problem-solving: Addresses and resolves issues related to format, footage quality, or software compatibility.
• Interdisciplinary collaboration: Works closely with Sound Designers, Directors, and other professionals to ensure coherence and integration of all video elements.
• Adapting to project needs: Tailors the edit to suit various styles, audiences, and communication objectives, depending on the type of product (advertising, documentary, music video, etc.).
Career and salary
A career as a Video Editor offers numerous opportunities for professional growth, with potential for specialisation in sectors such as film, television, advertising, and online video. Career progression can lead to more senior roles, such as Post-Production Supervisor or Creative Director.
Salaries vary depending on experience, project complexity, and geographical location, but are generally competitive within the audiovisual sector. With the rise of streaming platforms and increasing demand for video content, job prospects in this field are on the rise.

IED Open Days
We look forward to meeting you in person at our premises and online, to learn more about our teaching offerings, get to know our services and interact with coordinators, lecturers and students.
Skills and training
To become a skilled Video Editor, it’s essential to have a combination of technical and creative abilities. Proficiency in video editing software such as Adobe Premiere Pro, Final Cut Pro, and Avid Media Composer is crucial for managing the editing process effectively. In addition, knowledge of colour grading, sound design, and motion graphics can further enrich a Video Editor’s skill set.
Beyond technical skills, it’s important to develop artistic sensitivity and strong visual storytelling abilities to best interpret the creative vision of a project. Comprehensive training in this field can be gained through specialised courses in video production and editing. IED offers educational programmes that combine theory and practice, allowing students to gain hands-on experience through real-world projects and collaborations with industry professionals.
How to become a Video Editor
To embark on a career as a Video Editor, it is advisable to take specialised training courses and gain hands-on experience through internships or collaborations in the audiovisual field. This training pathway helps develop a solid understanding of editing techniques and production dynamics, honing the skills needed to produce high-quality video content.
If you’re ready to turn your passion for video editing into a professional career, explore IED’s courses in Video, Cinema, and Sound Design and begin your learning journey.